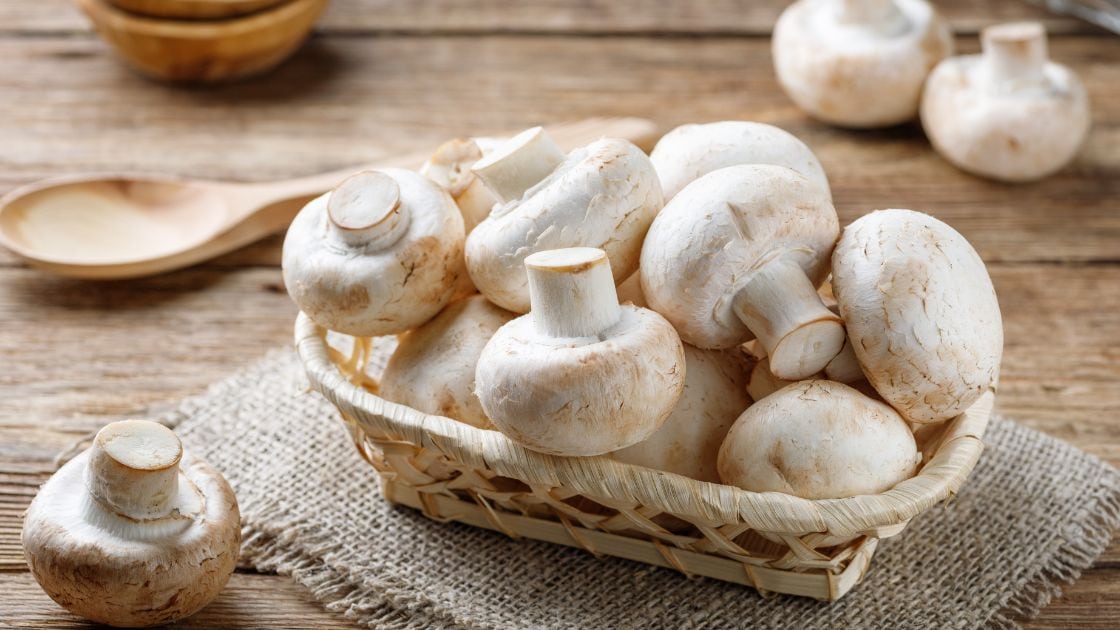
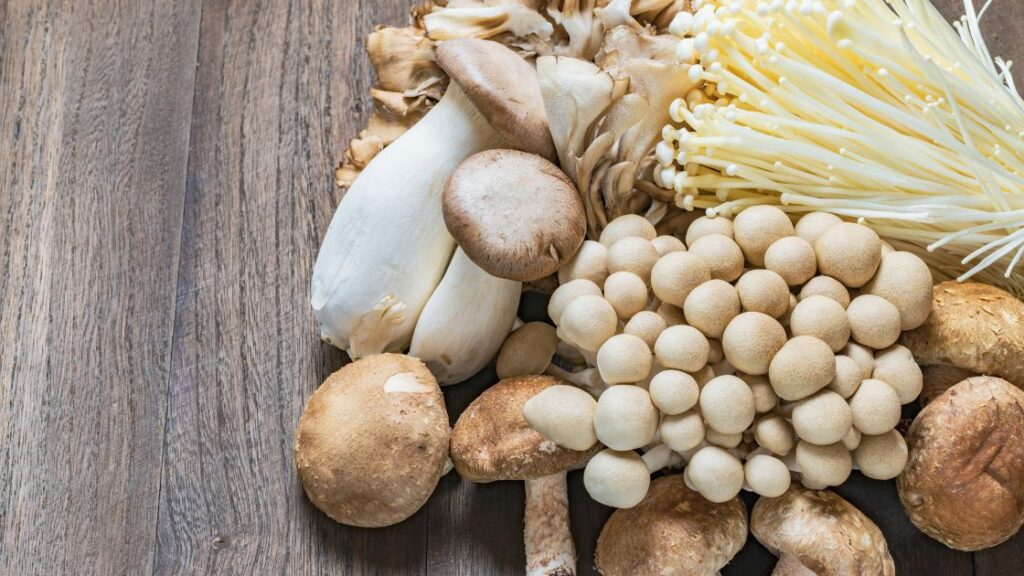
Mushrooms are a simple form of life known as fungus.
You can eat them with confidence, you will NOT get poisoned by eating them. They have a delicious flavor and a high nutritional value.
They are excellent sources of vitamins and minerals. Due to their therapeutic qualities, mushrooms are also helpful in the treatment of diseases and malnutrition.
Keep reading so that you know with us all its history and benefits and learn how to prepare mushroom recipes.
Physical description
Most mushrooms have a stalk or stem and a cap, typically shaped like a disc. The underside of the cap may have several closely spaced openings or pores that are known as gills.
The size and color of mushrooms vary widely, and some, like puffballs, don’t follow the stalk-and-cap design. A single mycelium can cover up to 1,500 acres of soil and is found below the surface. A mycelium is the parent organism of mushrooms.
History and production
The first time that mushrooms were used as food was by the Greeks. The first mushroom cultivation was introduced by Bonnefons in 1650.

In 1952, Culpeper’s book “Complete Herbal” was published, which included a section on mushroom cultivation. This was an important step in the history of mushrooms.
Was in the 1800s when the French began growing mushrooms underground in quarries near Paris. They used horse manure, mounded it up, and allowed it to heat up naturally for cultivation.
The technology for growing mushrooms was introduced to America by people from England, and France. These individuals began mushroom farming in a greenhouse in New York in the year 1885.
Cultivation and marketing of mushrooms have been maintained over time thanks to their important nutritional value. Know all the nutritional sources of this powerful food.
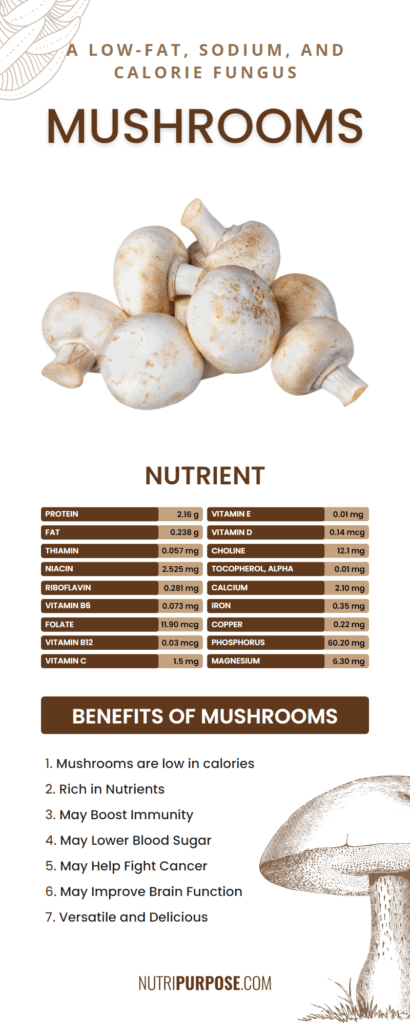
Nutrients of Mushrooms
Vitamins
- Thiamin [Vitamin B1] 0.057 mg – 5 % of DV
- Niacin [Vitamin B3] 2.525 mg – 16 % of DV
- Riboflavin [Vitamin B2] 0.281 mg – 22 % of DV
- Vitamin B6 0.073 mg – 4 % of DV
- Folate, DFE [Vitamin B9] 11.90 mcg – 3 % of DV
- Vitamin B12 [Cobalamin] 0.03 mcg – 1 % of DV
- Vitamin C [Ascorbic acid] 1.5 mg – 2 % of DV
- Folate, food 11.90 mcg
- Vitamin E (alpha-tocopherol) 0.01 mg – 0 % of DV
- Vitamin D 0.14 mcg – 1 % of DV
- Choline 12.1 mg – 2 % of DV
- Tocopherol, alpha 0.01 mg
Minerals
- Calcium 2.10 mg – 0 % of DV
- Iron 0.35 mg – 2 % of DV
- Copper 0.22 mg – 24 % of DV
- Phosphorus 60.20 mg – 5 % of DV
- Magnesium 6.30 mg – 2 % of DV
- Selenium 6.51 mcg – 12 % of DV
- Potassium 222.60 mg – 5 % of DV
- Zinc 0.36 mg – 3 % of DV
- Sodium 3.50 mg – 0 % of DV
Nutrients
- Fat 0.238 g – 0 % of DV
- Hexadecanoic acid 0.028 g
- Saturated fatty acids 0.035 g – 0 % of DV
- Polyunsaturated fatty acids 0.112 g
- Octadecanoic acid 0.007 g
- Octadecadienoic acid 0.112 g
Proteins and Aminoacids
- Protein 2.16 g – 4 % of DV
To complement a diet rich in protein, you can also eat spinach and asparagus.
Other Nutrient
- Water 64.72 g